Advantages of Using GIS in Legal Services
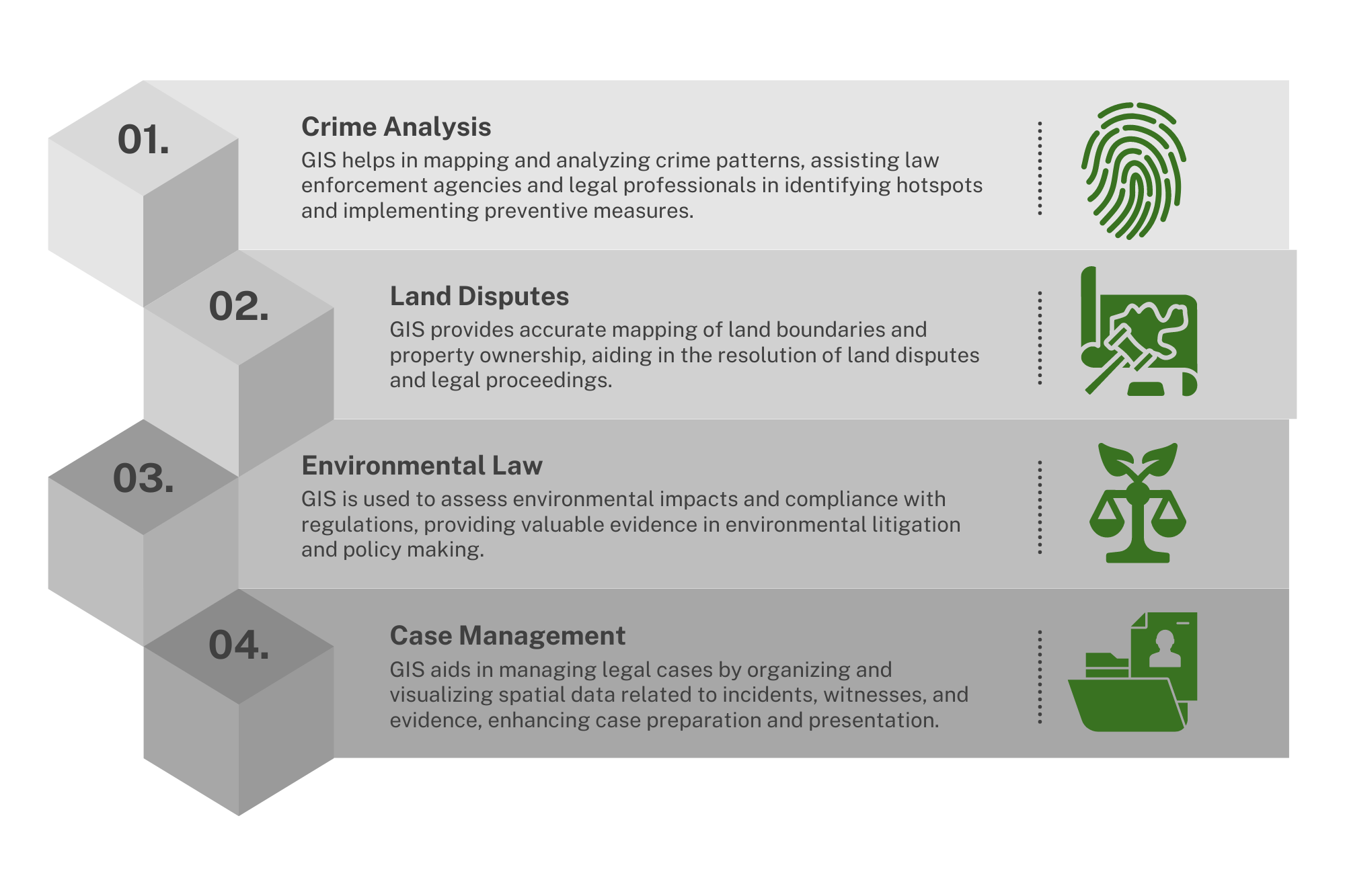
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) utilize spatial data to offer valuable insights and solutions for the legal industry. Incorporating GIS into your legal practice can enhance case strategy, improve efficiency, and provide unprecedented client services.
Key Features of GIS in Legal Industry
Enhanced Legal Research
Analyze geographical data to uncover patterns and insights relevant to cases involving environmental law, real estate, or other spatially related legal issues.
Optimized Case Management
Visualize case locations to better manage and allocate resources, including personnel and time, particularly for firms with a large geographical client base.
Client Service Improvement
Provide clients with visual insights into their cases, enhancing understanding and engagement.
Risk Management
Identify potential legal risks and compliance issues by analyzing geographical data related to zoning laws, environmental regulations, and other spatially dependent legislation.
Strategic Planning
Use spatial analysis to support litigation strategies, such as identifying trends in litigation locations or assessing jurisdictional advantages.
Case Studies
Enhancing Legal Research with GIS

Optimizing Case Management with GIS
Benefits of Implementing GIS in Legal Services
Efficiency Gains
Reduce time spent on research and case preparation by using GIS to quickly access and analyze relevant geographical data.
Improved Client Outcomes
Enhance case outcomes with comprehensive spatial analysis that can uncover unique insights and evidence.
Enhanced Decision Making
Make informed decisions with robust data visualization tools that offer a clearer understanding of the spatial factors at play.
Risk Mitigation
Proactively address potential legal issues by analyzing geographical data, thereby reducing the risk of non-compliance and litigation.
Client Satisfaction
Deliver superior client service with interactive maps and visual data that clarify complex legal scenarios, enhancing client understanding and involvement.
What Our Clients Say





Ready to Transform Your Legal Practice?
Contact us today to learn more about how GIS can revolutionize your legal operations and client services.
Frequently Asked Questions
GIS enhances case management by allowing legal professionals to visually organize and analyze case data geographically. This can help in understanding the spatial relationships and patterns related to case elements, which is particularly useful in managing real estate disputes, environmental law, and any case where location is pertinent. Moreover, GIS facilitates better allocation of resources by helping firms understand where their cases are concentrated geographically.
GIS offers unique benefits in legal research by providing the ability to overlay legal data with geographical maps. This can uncover insights in cases involving land use, zoning disputes, environmental regulation, and even historical property data. For example, attorneys can use GIS to track the historical ownership of a parcel of land, the environmental restrictions in a particular area, or the precedent of legal outcomes based on geographical factors.
Yes, GIS can significantly enhance client service by providing clients with a more interactive and engaging explanation of their cases. Through maps and spatial analysis, clients can better visualize the data and circumstances surrounding their cases, which helps in understanding complex legal issues and builds trust and transparency between the client and the law firm.
GIS contributes to risk management by providing lawyers with tools to foresee potential legal issues based on geographical data. This is especially valuable in compliance and regulatory practices where understanding the spatial aspects of regulations is crucial. GIS helps in identifying potential violations before they become costly legal problems, thus aiding in proactive legal advisement.
The costs associated with implementing GIS in legal services can vary based on several factors including the complexity of the GIS software, the scale of deployment, and the specific needs of the practice. Costs typically include software licensing fees, hardware investments (if not cloud-based), training for legal staff, and possibly consulting fees for initial setup and customization. Ongoing costs may involve software updates, data management, and technical support.
